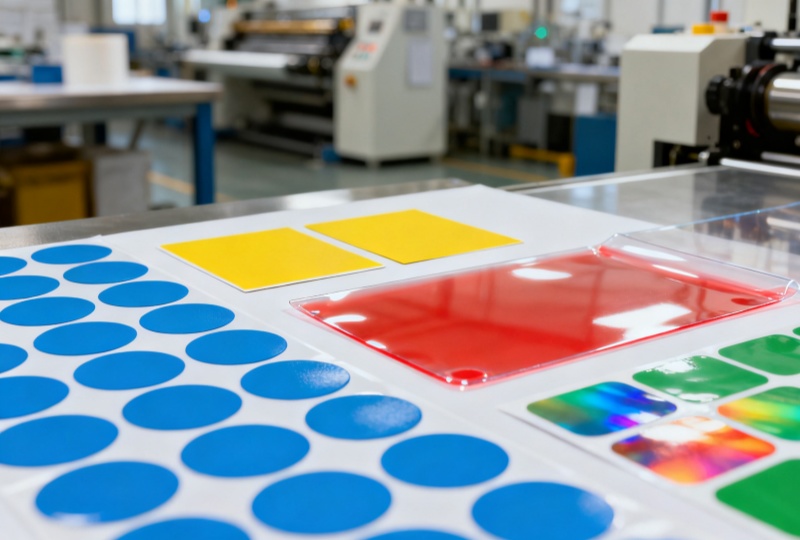
Self-Adhesive Labels vs Back Adhesives: PP Paper and PP Adhesive Paper Explained
In product labeling, choosing the right material is essential for performance and appearance. A self-adhesive label (pressure-sensitive) includes a printable face stock, a pressure-activated adhesive, and a release liner. In contrast, a back adhesive (transfer tape) is just a glue layer on a liner – it has no printed face. Likewise, polypropylene (PP) paper vs. PP back-adhesive paper differ in stickiness and usage.

At GemmyLabel, with over a decade of expertise in adhesive label solutions, we’re committed to helping you navigate these material choices with confidence. This comprehensive guide will explore the characteristics, applications, and advantages of each material, providing you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions for your specific needs.
What is a Self-Adhesive Label?
Structure and Composition
Self-adhesive labels, commonly known as pressure-sensitive labels, feature a sophisticated three-layer construction:
-
Face material: The printable surface (paper or film)
-
Adhesive layer: Pressure-sensitive glue
-
Release liner: Silicon-coated backing paper that protects the adhesive
This construction allows the label to be easily peeled from the backing and applied with minimal pressure to various surfaces.
Types and Applications
Self-adhesive labels come in several formats, each suited to different applications:
Paper-Based Self-Adhesive Labels
These cost-effective options are ideal for various applications, including:
-
Price tags and shipping labels
-
Pharmaceutical product information
-
Electronic equipment identification
-
Envelope addressing systems
Film-Based Self-Adhesive Labels
Made from materials like PE, PP, or PVC, these durable labels are available in white, matte, or transparent finishes. They offer superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, making them suitable for:
-
Food packaging and beverage containers
-
Cosmetic and personal care products
-
Outdoor equipment labeling
-
Industrial product identification
Table: Self-Adhesive Label Materials and Their Applications
| Material Type | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Paper Labels | Cost-effective, recyclable, writable | Dry products, shipping labels, and office use |
| White BOPP | Waterproof, tear-proof, oil-resistant | Food packaging, refrigerated items, and beverages |
| Clear BOPP | Transparent “no-label” look | Product packaging where design shows through |
| Foil Labels | Metallic sheen, premium appearance | Gourmet foods, cosmetics, and high-end products |
What is a Back Adhesive (Glue Tape)?
Understanding Back Glue Structure
Unlike self-adhesive labels with their three-layer construction, back glue consists simply of a glue layer and a release liner. There is no face material, making it essentially a layer of adhesive on a protective backing. The release liner is typically coated with silicone on both sides to prevent the adhesive from sticking prematurely.
Key Differences from Self-Adhesive Labels
The fundamental distinction lies in their composition and application:
-
Self-adhesive labels have a printed face material and are designed to be the visible element
-
Back glue is purely an adhesive layer used to stick two surfaces together
-
Self-adhesive labels are typically smaller and used for informational purposes
-
Back glue is generally applied in larger sheets for mounting purposes
Common Applications of Back Glue
Back glue functions similarly to double-sided tape and is commonly used for:
-
Mounting posters and large displays
-
Applying PP paper to various surfaces
-
Temporary installations requiring strong adhesion
-
Industrial applications where two surfaces need bonding
PP Paper and PP Adhesive Paper: The Versatile Display Materials
PP Paper (Photo Paper)
PP paper, also known as photo paper or poster paper, is a printable material without any adhesive backing. It’s essentially a high-quality white paper designed for high-resolution printing, but it lacks any inherent sticking capability. Sometimes used for product packaging, this material requires an additional adhesive if mounting is necessary.
PP Adhesive Paper (PP Back Glue Paper)
PP adhesive paper is essentially PP paper with an added self-adhesive backing, making it similar to self-adhesive labels but typically used in larger formats. This material features:
-
A printable front surface suitable for high-quality graphics
-
A pressure-sensitive adhesive layer
-
A removable protective liner that covers the adhesive until application
This combination creates what’s known as “adhesive photo paper” or “back glue photo paper,” which is significantly thicker than conventional stickers—often about twice the thickness of standard sticker paper.
Applications and Limitations
Both PP paper and PP adhesive paper are primarily indoor materials that can fade when exposed to direct sunlight. Their primary applications include:
-
Exhibition displays and trade show graphics
-
Retail signage and point-of-purchase displays
-
Indoor banners and posters
-
Educational materials and presentation graphics
-
Temporary promotional materials
Material Selection Guide: Choosing the Right Solution
Consider Your Surface Characteristics
The surface you’re applying to significantly influences your material choice:
-
Smooth, flat surfaces: Most materials adhere well
-
Curved or contoured surfaces: Flexible films like BOPP work best
-
Textured surfaces: More aggressive adhesives may be necessary
-
Non-porous surfaces (glass, plastic): Film-based materials with permanent adhesives
-
Porous surfaces (cardboard, wood): Paper-based materials adhere well
Evaluate Environmental Conditions
The environment your label will face determines the material requirements:
For outdoor or harsh environments:
-
Waterproof materials like BOPP
-
UV-resistant coatings to prevent fading
-
Temperature-resistant adhesives
-
Laminates for added protection
For indoor applications:
-
Cost-effective paper materials
-
Matte or glossy finishes based on aesthetic preferences
-
Standard permanent adhesives
Application Method Considerations
Your labeling process should influence material selection:
-
Hand application: Repositionable adhesives facilitate placement
-
Machine application: Consistent liner tension and die-cutting are critical
-
High-volume applications: Roll labels improve efficiency
-
Precision placement: Kiss-cut labels protect intricate shapes
Specialized Requirements
Different industries have unique labeling needs:
Food Packaging
-
Waterproof and oil-resistant materials like BOPP or PET
-
Compliance with food safety regulations
-
Temperature resistance for refrigeration or freezing
Product Branding
-
Premium materials like foil or metallic BOPP for luxury items
-
Custom shapes to enhance brand recognition
-
Durable materials that maintain appearance throughout product life
Logistics and Shipping
-
Paper labels for cost-effectiveness
-
Permanent adhesives that withstand handling
-
Printable surfaces for variable information
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice Matters
Understanding the differences between self-adhesive labels, back glue, PP paper, and PP adhesive paper empowers you to make informed decisions that enhance your projects’ effectiveness and longevity. Each material serves distinct purposes, and selecting the appropriate one ensures better adhesion, appearance, and performance.
The team at GemmyLabel combines technical expertise with creative solutions to deliver labels that protect your products, comply with regulations, and captivate consumers. Our commitment to quality, customization, and customer support makes us the ideal partner for businesses looking to make their mark in their industry.
Ready to transform your product presentation with the perfect labeling solution? Contact GemmyLabel today to discuss your custom label needs and discover how our expertise can help your products stand out in a competitive marketplace.